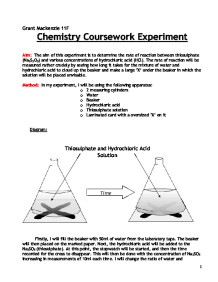
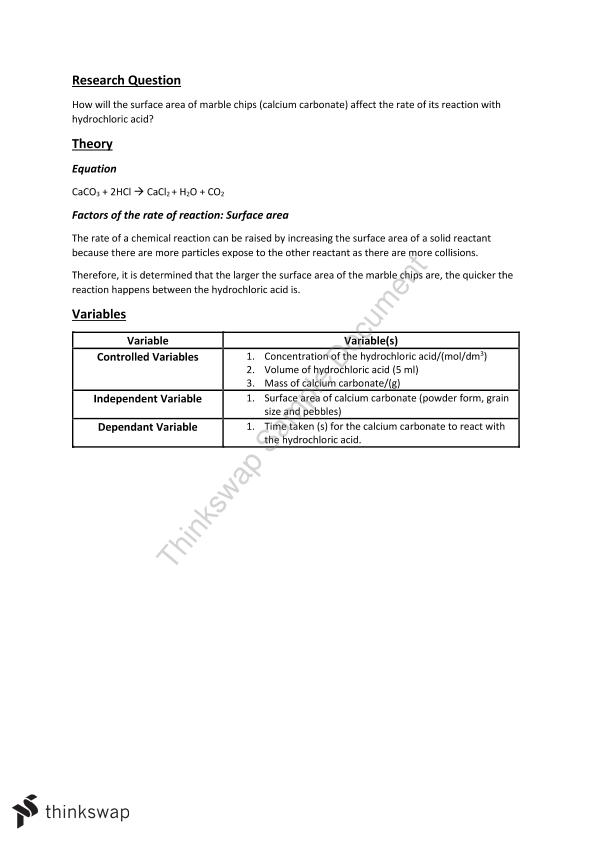
Marble Chips And Hydrochloric Acid Experiment Method

An outline of an experiment that could be used to find the time and hence rate of reaction of marble chips and hydrochloric acid.
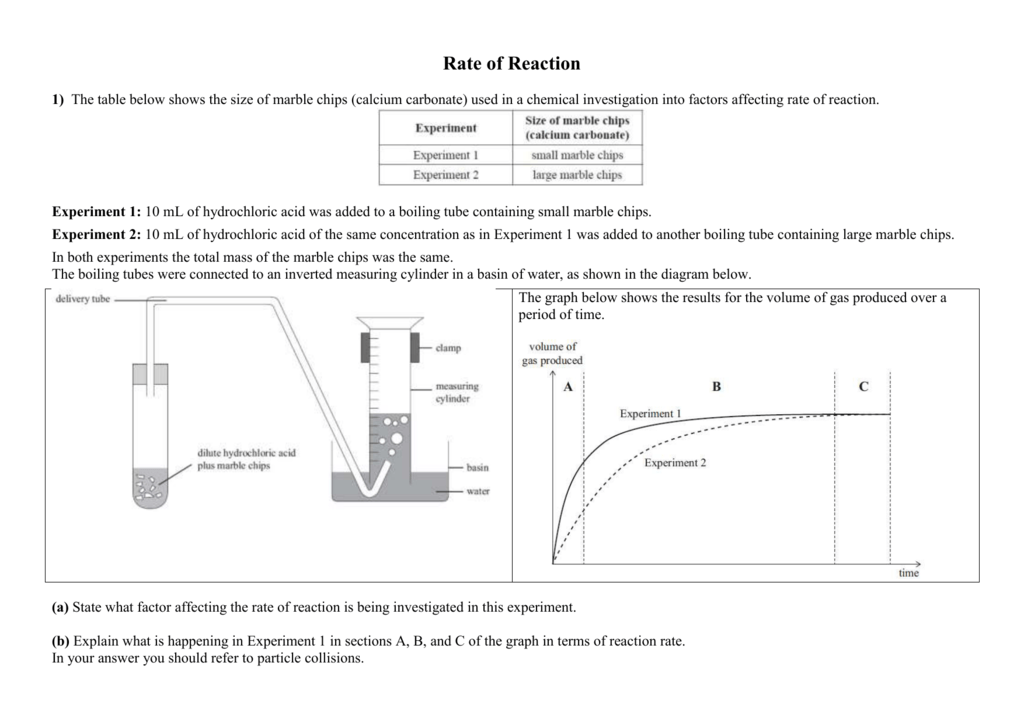
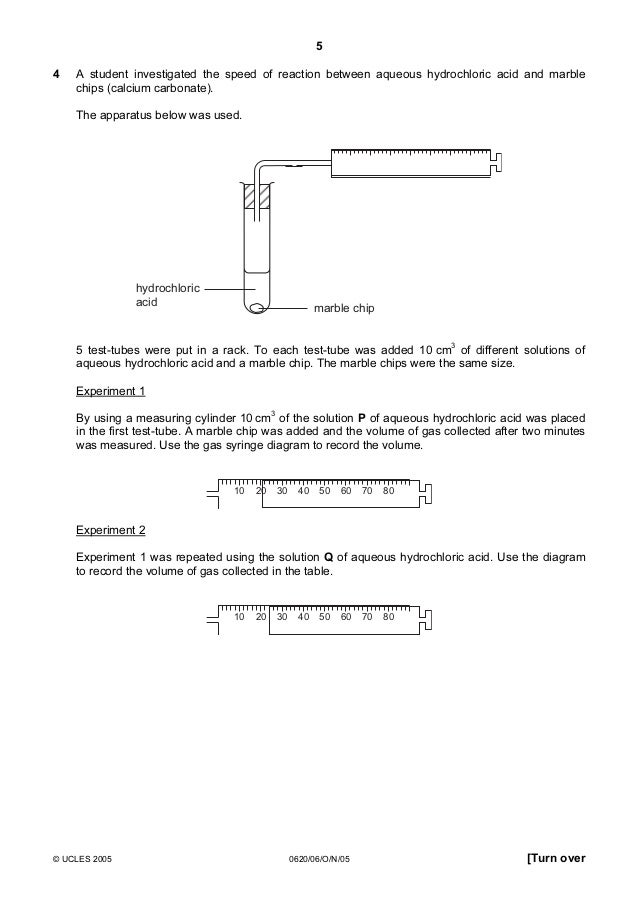
Marble chips and hydrochloric acid experiment method. Using the apparatus shown the change in mass of carbon dioxide can be measure with time. Measured out 1ml of water in a 10ml measuring cylinder and placed into the test tube labelled 2. To start the reaction the flask is gently lent to one side causing the card to fall and the marble chips and acid to mix. Marble chips and acid are placed in the flask but separated by a piece of card preventing the reaction from proceeding.
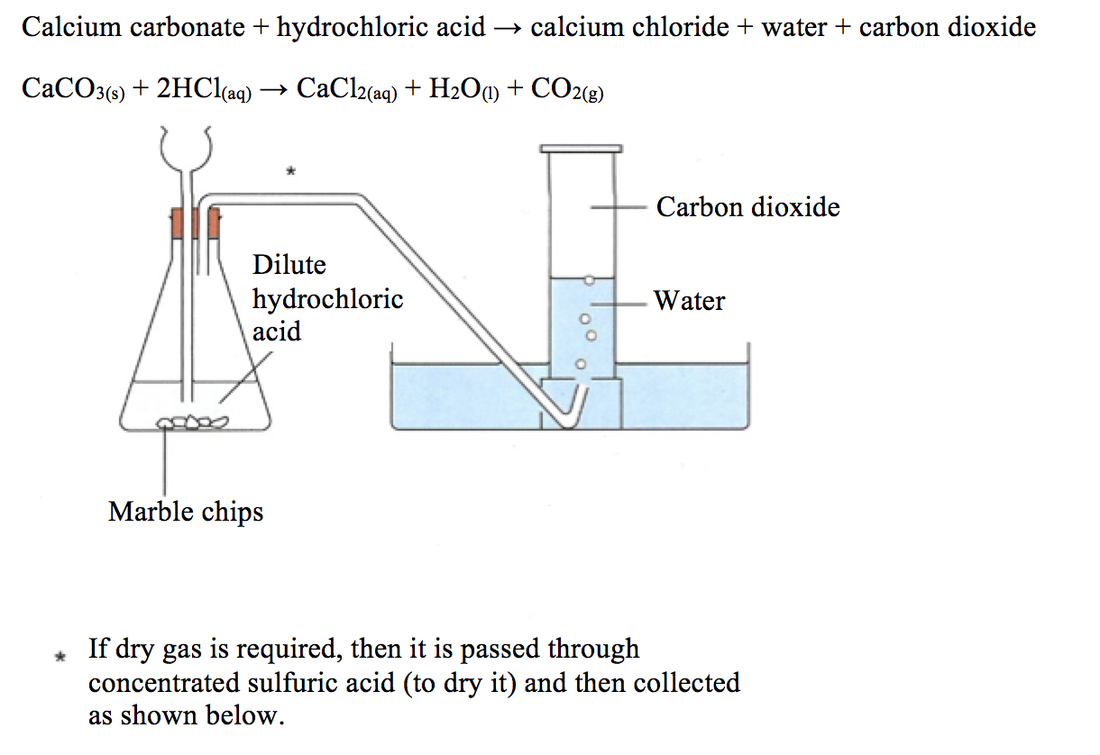
Calcium chloride solution is also formed. An investigation of the reaction between marble chips and hydrochloric acid. Marble chips react with dilute hydrochloric acid to produce carbon dioxide gas. Cacl2 aq h2o l co2 g in this experiment i am going to see if temperature affects the reaction rate between marble chips and hydrochloric acid by timing the release of carbon dioxide in the reaction.
I predict the higher the temperature the. Hydrochloric acid marble chips the experiment the aim of this experiment is to find out how different variables affect the rate at which the reaction between marble chips caco and hydrochloric acid hcl takes place. Marble is calcium carbonate and thus behaves in the same way. Marble chips placed onto pieces of paper.
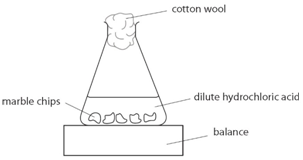
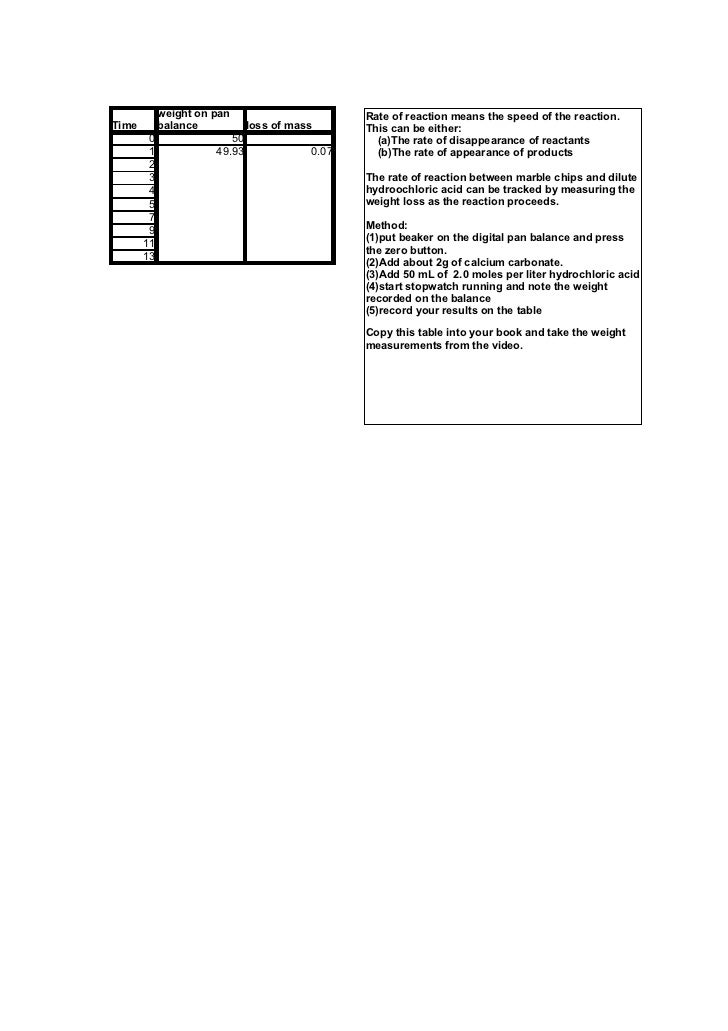
Plugged in scientific scales and weighed out 1g of marble chips for each test tube. Measured 5ml of hydrochloric acid in the 10ml measuring cylinders and placed into each beaker separately. This apparatus is placed on a balance and the mass of the flask and its contents is read. In high concentrated acid the particles of the marble chip will move faster due to the more collisions between the particles of marble chips and the acid.
The rate of this reaction can be changed by changing the size of the marble chips. This is due to the collision theory. I predict the higher the concentration of hydrochloric acid faster the reaction rate and more carbon dioxide will be produced as the time increases. Caco3 s 2hcl aq 61614.